Howard Becker, a General Electric engineer, invented the first supercapacitors in the 1950s. NEC gave this name in 1978, and the device was utilized as a kind of backup power for computer memory.
They may now be found in laptops, GPS systems, portable computers, camera flashes, and a variety of other electronic gadgets.
They are also now finding a home in the hybrid and electric Vehicles as they’re ideal for collecting and releasing the electricity generated by regenerative braking, which is a dynamic short-term load.
Supercapacitors can also be used in vehicles like public transportation buses or trams as these modes simply require enough power to go to the next stop, where they will be recharged in seconds or minutes.

Since they don’t really wear down, as they can be charged and emptied in excess of a million times with no degradation, this fixed public transport cycle makes a lot of sense for this technology.
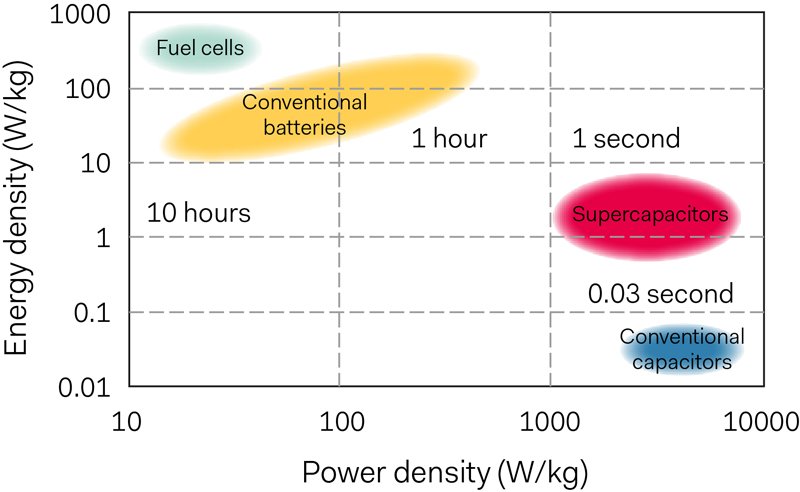
With the current state of research, it is likely that we will one day have supercapacitor batteries. These would be devices with the durability and speed of ultracapacitors but the energy density and operating duration of batteries.
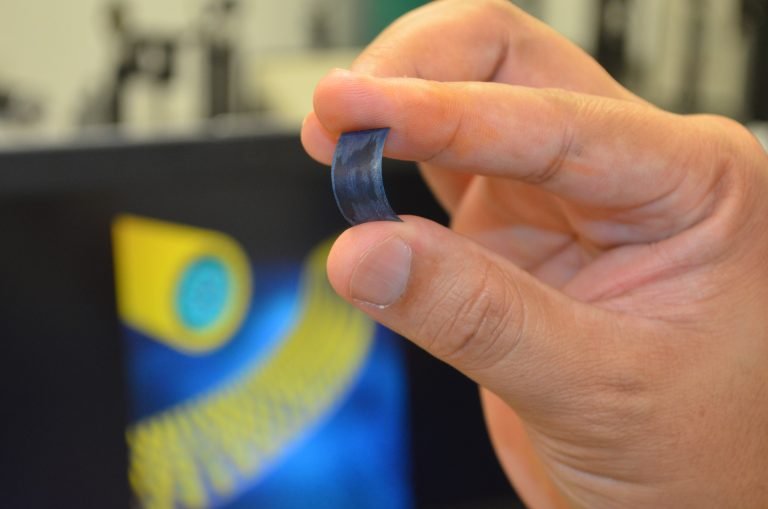

In 2016, scientists at the University of Central Florida developed a prototype flexible supercapacitor with a greater energy density than existing and a charge cycle life of 30,000 cycles without deterioration.
New nanoscale materials and graphene tests all lead to the development of supercapacitors with substantially greater energy densities. Though they are not yet a replacement for lithium-ion batteries but they are now ideal for an increasing variety of electronic devices.
Reference- Journal ACS Nano, How-To Geeks, Science Alert, Inside EVs






