IIT Madras researchers are working on a new type of zinc– air battery technology for electric cars that might be a viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries. The ability to charge the zinc – air battery mechanically is a vital feature.

The researchers have applied for patents and are collaborating with key enterprises to ensure the orderly development of this zinc-air battery technology. When compared to lithium-ion batteries, the zinc-air battery is also less expensive and has a longer shelf life.
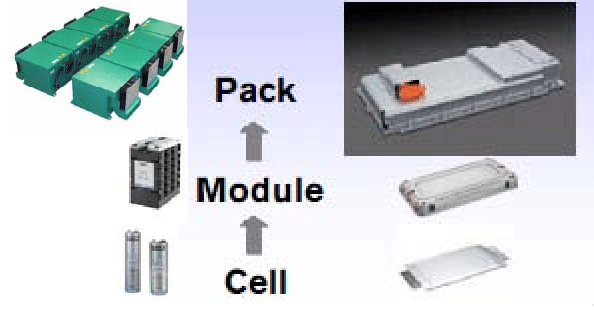
They are transitioning zinc-air battery technology from “cells” to “pack” systems. The researchers may also focus on creating separate zinc – air battery recharge stations that will function similarly to any other fuel station, since this technology is based on ‘Battery Swapping’ in which Vehicle Users can swap used ‘zinc cassettes’ of the battery with fully-charged ‘zinc cassettes’ at these ‘Zinc recharge stations.’
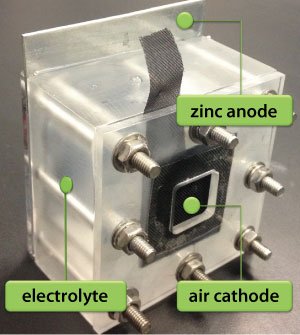
Furthermore, the technique is far less expensive than lithium-ion batteries as in lithium the entire used battery pack has to be removed and be swapped with a complete lithium-ion battery pack. This results in double the capital investment in the case of lithium-ion batteries but in this case only the zinc cassettes has to be removed.
Zinc-air battery technologies have the potential to be a wonderful alternative to lithium, reducing India’s EV industry’s reliance on China for lithium-ion battery imports.
Because batteries account for 40-50 percent of the cost of electric cars in India, experts believe that local technology research and production would reduce costs and open the way for speedier EV adoption in the nation.
Reference- IIT Madras Media Release, NDTV, Mercom India, Science News, Business Standard, The New Indian Express






