According to a news statement from the Earth Institute at Columbia University, a major portion of the Larsen Ice Shelf in Antarctica, called “Larsen-B,” has broken out into the ocean. Since the size of this Antarctic ice is the same as that of Philadelphia, sea levels may increase. This sudden breaking has exposed fragile glaciers to the sea, hastening melting.
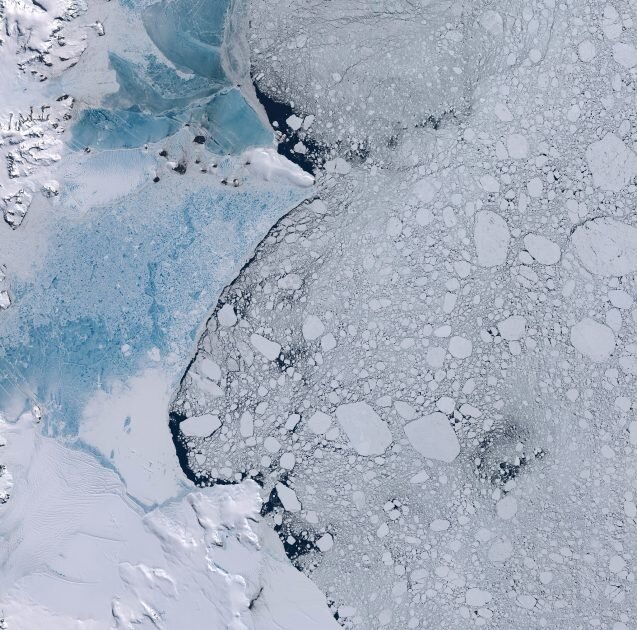

Previously, the ice shelf served to shelter several glaciers around the Antarctic Peninsula from the sea. However, experts warn that the glaciers are now vulnerable to faster melt, which may cause sea levels to rise much more.
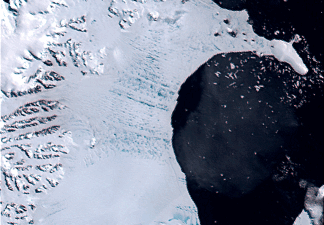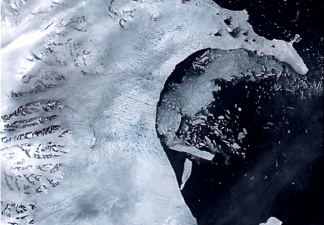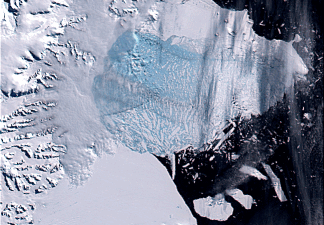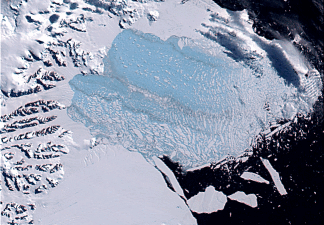
A multinational team of scientists behind a recent research on this disintegration is still puzzled as to why the Larsen-B ice shelf cracked so swiftly. It’s impossible to say what triggered the breakdown because the sea ice was already cracked previous to the split. However, some feel that rising summer temperatures and winds delivering warm air are to blame.
Regardless of why it disintegrated, the event now poses a major threat to the glaciers it formerly protected. The Larsen-B ice shelf used to buttress the glaciers, preventing water from forcing them into the sea and reducing their impact to sea level rise. The glaciers are now exposed and at risk of melting quicker as a result of its removal.
Unfortunately, this is simply another bleak illustration of manmade climate change in action.
Reference- Delft University of Technology, journal Remote Sensing of Environment, Futurism, NASA Satellite Image






